核心思想
A 星算法
A*算法,指定源点,指定目标点,求源点到达目标点的最短距离 增加了当前点到终点的预估函数 在堆中根据从源点出发到达当前点的距离+当前点到终点的预估距离来进行排序 剩下的所有细节和 Dijskra 算法完全一致
预估函数要求:当前点到终点的预估距离 <= 当前点到终点的真实最短距离 预估函数是一种吸引力 1)合适的吸引力可以提升算法的速度,吸引力过强会出现错误 2)保证预估距离 <= 真实最短距离的情况下,尽量接近真实最短距离,可以做到功能正确且最快
预估终点距离经常选择: 曼哈顿距离 欧式距离 对角线距离
模版代码:
public static int[]move=new int[]{-1,0,1,0,-1};
// A*算法
// grid[i][j] == 0 代表障碍
// grid[i][j] == 1 代表道路
// 只能走上、下、左、右,不包括斜线方向
// 返回从(startX, startY)到(targetX, targetY)的最短距离
public static int aStarDistance(int[][] grid, int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
//出发点或者目标点是障碍的时候
if(grid[startX][startY]==0 || grid[targetX][targetY]==0){
return -1;
}
int n=grid.length;
int m=grid[0].length;
int[][]distance=new int[n][m];
boolean[][]visited=new boolean[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
visited[i][j]=false;
}
}
PriorityQueue<int[]>heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->a[2]-b[2]);
distance[startX][startY]=1;
heap.add(new int[]{startX,startY,distance[startX][startY]+f1(startX,startY,targetX,targetY)});
while (!heap.isEmpty()){
int []record=heap.poll();
int x=record[0];
int y=record[1];
if(visited[x][y]){
continue;
}
visited[x][y]=true;
if(x==targetX && y==targetY){
return distance[x][y];
}
//向上下左右四个方向移动
for(int i=0,nx,ny;i<4;i++){
nx=x+move[i];
ny=y+move[i+1];
if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m && grid[nx][ny]==1 && !visited[nx][ny] && distance[x][y]+1<distance[nx][ny]){
distance[nx][ny]=distance[x][y]+1;
heap.add(new int[]{nx,ny,distance[nx][ny]+f1(nx,ny,targetX,targetY)});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
//接下来是3种常见的预估函数
//曼哈顿距离
public static int f1(int x,int y,int targetX,int targetY){
return (Math.abs(targetX-x)+Math.abs(targetY-y));
}
// 对角线距离
public static int f2(int x, int y, int targetX, int targetY) {
return Math.max(Math.abs(targetX - x), Math.abs(targetY - y));
}
// 欧式距离
public static double f3(int x, int y, int targetX, int targetY) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(targetX - x, 2) + Math.pow(targetY - y, 2));
}Floyd 算法
Floyd 算法,得到图中任意两点之间的最短距离 时间复杂度 O (n^3),空间复杂度 O (n^2),常数时间小,容易实现 适用于任何图,不管有向无向、不管边权正负、但是不能有负环(保证最短路存在)
过程简述: Distance [ i ] [ j ] 表示 i 和 j 之间的最短距离 Distance[i] [j] = min ( distance[i] [j] , distance[i] [k] + distance[k] [j]) 枚举所有的 k 即可,实现时一定要最先枚举跳板!
模版代码
public static void floyd(){
for(int bridge=0;bridge<n;bridge++){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(distance[i][bridge]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE && distance[bridge][j]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE
&& distance[i][bridge]+distance[bridge][j]<distance[i][j]){
distance[i][j]=distance[i][bridge]+distance[bridge][j];
}
}
}
}
}Bellman-Ford 算法
Bellman-Ford 算法,解决可以有负权边但是不能有负环(保证最短路存在)的图,单源最短路算法
松弛操作 假设源点为 A,从 A 到任意点 F 的最短距离为 distance[F] 假设从点 P 出发某条边,去往点 S,边权为 W 如果发现,distance[P] + W < distance[S],也就是通过该边可以让 distance[S]变小 那么就说,P 出发的这条边对点 S 进行了松弛操作
Bellman-Ford 过程 1,每一轮考察每条边,每条边都尝试进行松弛操作,那么若干点的 distance 会变小 2,当某一轮发现不再有松弛操作出现时,算法停止
Bellman-Ford 算法时间复杂度 假设点的数量为 N,边的数量为 M,每一轮时间复杂度 O (M) 最短路存在的情况下,因为 1 次松弛操作会使 1 个点的最短路的边数+1 而从源点出发到任何点的最短路最多走过全部的 n 个点 ,n 个点即 n-1 条边,所以松弛的轮数必然 <= n - 1 所以 Bellman-Ford 算法时间复杂度 O (M*N)
重要推广:判断从某个点出发能不能到达负环 上面已经说了,如果从 A 出发存在最短路(没有负环),那么松弛的轮数必然 <= n - 1 而如果从 A 点出发到达一个负环,那么松弛操作显然会无休止地进行下去 所以,如果发现从 A 点出发,在第 n 轮时松弛操作依然存在,说明从 A 点出发能够到达一个负环
Bellman-Ford+SPFA 优化
Bellman-Ford + SPFA 优化(Shortest Path Faster Algorithm) 很轻易就能发现,每一轮考察所有的边看看能否做松弛操作是不必要的 因为只有上一次被某条边松弛过的节点,所连接的边,才有可能引起下一次的松弛操作 所以用队列来维护 “这一轮哪些节点的 distance 变小了” 下一轮只需要对这些点的所有边,考察有没有松弛操作即可
SPFA 只优化了常数时间,在大多数情况下跑得很快,但时间复杂度为 O (n*m) 看复杂度就知道只适用于小图,根据数据量谨慎使用,在没有负权边时要使用 Dijkstra 算法
Bellman-Ford + SPFA 优化的用途
1)适用于小图
2)解决有负边(没有负环)的图的单源最短路径问题
3)可以判断从某个点出发是否能遇到负环,如果想判断整张有向图有没有负环,需要设置虚拟源点
4)并行计算时会有很大优势,因为每一轮多点判断松弛操作是相互独立的,可以交给多线程处理
例题
1、对数器测试 A*
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code01_AStarAlgorithm
* @description:
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-26 10:13
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class065;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Code01_AStarAlgorithm {
public static int[]move=new int[]{-1,0,1,0,-1};
// A*算法
// grid[i][j] == 0 代表障碍
// grid[i][j] == 1 代表道路
// 只能走上、下、左、右,不包括斜线方向
// 返回从(startX, startY)到(targetX, targetY)的最短距离
public static int aStarDistance(int[][] grid, int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
//出发点或者目标点是障碍的时候
if(grid[startX][startY]==0 || grid[targetX][targetY]==0){
return -1;
}
int n=grid.length;
int m=grid[0].length;
int[][]distance=new int[n][m];
boolean[][]visited=new boolean[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
visited[i][j]=false;
}
}
PriorityQueue<int[]>heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->a[2]-b[2]);
distance[startX][startY]=1;
heap.add(new int[]{startX,startY,distance[startX][startY]+f1(startX,startY,targetX,targetY)});
while (!heap.isEmpty()){
int []record=heap.poll();
int x=record[0];
int y=record[1];
if(visited[x][y]){
continue;
}
visited[x][y]=true;
if(x==targetX && y==targetY){
return distance[x][y];
}
//向上下左右四个方向移动
for(int i=0,nx,ny;i<4;i++){
nx=x+move[i];
ny=y+move[i+1];
if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m && grid[nx][ny]==1 && !visited[nx][ny] && distance[x][y]+1<distance[nx][ny]){
distance[nx][ny]=distance[x][y]+1;
heap.add(new int[]{nx,ny,distance[nx][ny]+f1(nx,ny,targetX,targetY)});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
//接下来是3种常见的预估函数
//曼哈顿距离
public static int f1(int x,int y,int targetX,int targetY){
return (Math.abs(targetX-x)+Math.abs(targetY-y));
}
// 对角线距离
public static int f2(int x, int y, int targetX, int targetY) {
return Math.max(Math.abs(targetX - x), Math.abs(targetY - y));
}
// 欧式距离
public static double f3(int x, int y, int targetX, int targetY) {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(targetX - x, 2) + Math.pow(targetY - y, 2));
}
// Dijkstra算法
// grid[i][j] == 0 代表障碍
// grid[i][j] == 1 代表道路
// 只能走上、下、左、右,不包括斜线方向
// 返回从(startX, startY)到(targetX, targetY)的最短距离
public static int dijkstra(int[][] grid, int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
if (grid[startX][startY] == 0 || grid[targetX][targetY] == 0) {
return -1;
}
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
int[][] distance = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
distance[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
distance[startX][startY] = 1;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
// 0 : 行
// 1 : 列
// 2 : 从源点出发到达当前点的距离
heap.add(new int[] { startX, startY, 1 });
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = heap.poll();
int x = cur[0];
int y = cur[1];
if (visited[x][y]) {
continue;
}
visited[x][y] = true;
if (x == targetX && y == targetY) {
return distance[x][y];
}
for (int i = 0, nx, ny; i < 4; i++) {
nx = x + move[i];
ny = y + move[i + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && grid[nx][ny] == 1 && !visited[nx][ny]
&& distance[x][y] + 1 < distance[nx][ny]) {
distance[nx][ny] = distance[x][y] + 1;
heap.add(new int[] { nx, ny, distance[x][y] + 1 });
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static int[][] randomGrid(int n) {
int[][] grid = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (Math.random() < 0.3) {
// 每个格子有30%概率是0
grid[i][j] = 0;
} else {
// 每个格子有70%概率是1
grid[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
return grid;
}
// 为了测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len = 100;
int testTime = 10000;
System.out.println("功能测试开始");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int n = (int) (Math.random() * len) + 2;
int[][] grid = randomGrid(n);
int startX = (int) (Math.random() * n);
int startY = (int) (Math.random() * n);
int targetX = (int) (Math.random() * n);
int targetY = (int) (Math.random() * n);
int ans1 = dijkstra(grid, startX, startY, targetX, targetY);
int ans2 = aStarDistance(grid, startX, startY, targetX, targetY);
if (ans1 != ans2) {
System.out.println("出错了!");
}
}
System.out.println("功能测试结束");
System.out.println("性能测试开始");
int[][] grid = randomGrid(4000);
int startX = 0;
int startY = 0;
int targetX = 3900;
int targetY = 3900;
long start, end;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int ans1 = dijkstra(grid, startX, startY, targetX, targetY);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行dijskra算法结果: " + ans1 + ", 运行时间(毫秒) : " + (end - start));
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int ans2 = aStarDistance(grid, startX, startY, targetX, targetY);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行A*算法结果: " + ans2 + ", 运行时间(毫秒) : " + (end - start));
System.out.println("性能测试结束");
}
}2、明显危险 S
题目描述 农夫约翰正驾驶一条小艇在牛勒比海上航行。
海上有 N(1\leq N\leq 100) 个岛屿,用 1 到 N 编号。约翰从 1 号小岛出发,最后到达 N 号小岛。
一张藏宝图上说,如果他的路程上经过的小岛依次出现了 A_1,A_2,\dots ,A_M(2\leq M\leq 10000) 这样的序列(不一定相邻),那他最终就能找到古老的宝藏。但是,由于牛勒比海有海盗出没,约翰知道任意两个岛屿之间的航线上海盗出没的概率,他用一个危险指数 D_{i,j}(0\leq D_{i,j}\leq 100000) 来描述。他希望他的寻宝活动经过的航线危险指数之和最小。那么,在找到宝藏的前提下,这个最小的危险指数是多少呢?
输入格式
第一行:两个用空格隔开的正整数 N 和 M。
第二到第 M+1 行:第 i+1 行用一个整数 A_i 表示 FJ 必须经过的第 i 个岛屿。保证 A_1=1,A_M=N。
第 M+2 到第 N+M+1 行:第 i+M+1 行包含 N 个用空格隔开的非负整数分别表示 i 号小岛到第 1\dots N 号小岛的航线各自的危险指数。保证第 i 个数是 0。
输出格式
第一行:FJ 在找到宝藏的前提下经过的航线的危险指数之和的最小值。
输入输出样例
输入
3 4
1
2
1
3
0 5 1
5 0 2
1 2 0输出
7说明/提示
样例说明 这组数据中有三个岛屿,藏宝图要求 FJ 按顺序经过四个岛屿:1 号岛屿、2 号岛屿、回到 1 号岛屿、最后到 3 号岛屿。每条航线的危险指数也给出了:航路 (1,2),(2,3),(3,1) 和它们的反向路径的危险指数分别是 5,2,1。
FJ 可以通过依次经过 1,3,2,3,1,3 号岛屿以 7 的最小总危险指数获得宝藏。这条道路满足了奶牛地图的要求 (1,2,1,3)。我们避开了 1 号和 2 号岛屿之间的航线,因为它的危险指数太大了。
注意:测试数据中 a 到 b 的危险指数不一定等于 b 到 a 的危险指数!
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code02_Floyd
* @description:Floyd算法模版(洛谷)
* // 测试链接 : https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2910
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-26 10:45
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class065;
import java.io.*;
public class Code02_Floyd {
public static int MAXN=101;
public static int MAXM=10001;
public static int n,m;
public static int[][]distance=new int[MAXN][MAXN];
public static int[]path=new int[MAXM];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in=new StreamTokenizer(bufferedReader);
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while (in.nextToken()!=StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF){
n=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
m=(int)in.nval;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
in.nextToken();
path[i]=(int)in.nval-1;
}
build();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
in.nextToken();
distance[i][j]=(int)in.nval;
}
}
//运行floyd算法
floyd();
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++){
ans+=distance[path[i]][path[i+1]];
}
out.println(ans);
}
out.flush();
out.close();
bufferedReader.close();
}
public static void build(){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
}
public static void floyd(){
for(int bridge=0;bridge<n;bridge++){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(distance[i][bridge]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE && distance[bridge][j]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE
&& distance[i][bridge]+distance[bridge][j]<distance[i][j]){
distance[i][j]=distance[i][bridge]+distance[bridge][j];
}
}
}
}
}
}3、K 站中转内最便宜的航班
题目描述: 有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。
现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线,使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
示例 1:
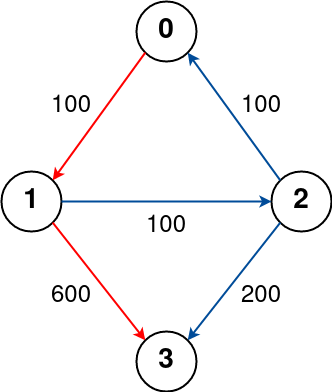
输入: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1 输出: 700 解释: 城市航班图如上 从城市 0 到城市 3 经过最多 1 站的最佳路径用红色标记,费用为 100 + 600 = 700。 请注意,通过城市 [0, 1, 2, 3] 的路径更便宜,但无效,因为它经过了 2 站。
示例 2:
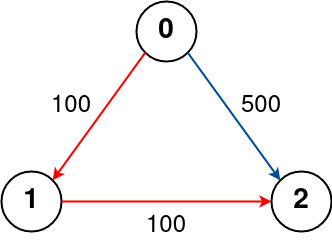
输入: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1 输出: 200 解释: 城市航班图如上 从城市 0 到城市 2 经过最多 1 站的最佳路径标记为红色,费用为 100 + 100 = 200。
示例 3:
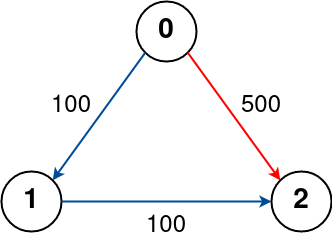
输入:n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0 输出:500 解释: 城市航班图如上 从城市 0 到城市 2 不经过站点的最佳路径标记为红色,费用为 500。
这题用 Bellman-Ford 算法,但是不能直接用,需要修改下:
这里因为题目,要与最原本的 Bellman-Ford 算法有所修改,但整体还是 Bellman-Ford 算法的骨架
将 Bellman-Ford 算法原本的松弛轮数替换为飞机转程次数 K ,但是原本的 Bellman-Ford 算法在一轮循环中可能松弛多次,无法与题意的 K 次相互对应
这里为了让每轮松弛只松弛一次,我们设定两个距离数组,当前更新时使用的距离数组 cur(cur 是上一轮更新完的),以及当前轮更新后给下一轮使用的 next
即所有的目的是不让当前轮新更的距离在当前轮中使用,这样保证每轮只会松弛一次
这题的代码也不好作为 Bellman-Ford 算法的模版代码
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code03_BellmanFord
* @description: Bellman-Ford算法应用(不是模版)
* // k站中转内最便宜的航班
* // 有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组 flights
* // 其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei]
* // 表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 pricei 抵达 toi。
* // 现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过 k 站中转的路线
* // 使得从 src 到 dst 的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出 -1。
* // 测试链接 : https://leetcode.cn/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-27 12:49
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class065;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Code03_BellmanFord {
class Solution {
//使用Bellman-Ford 算法
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
//每轮松弛时,当前所用的距离数组
int[]cur=new int[n];
Arrays.fill(cur,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
cur[src]=0;
//这里因为题目,要与最原本的Bellman-Ford 算法有所修改,但整体还是Bellman-Ford 算法的骨架
//将Bellman-Ford 算法原本的松弛轮数替换为飞机转程次数K
//但是原本的Bellman-Ford 算法在一轮循环中可能松弛多次,无法与题意的K次相互对应
//这里为了让每轮松弛只松弛一次,我们设定两个距离数组
//当前更新时使用的距离数组cur(cur是上一轮更新完的),以及当前轮更新后给下一轮使用的next
//即所有的的目的是不让当前轮新更的距离在当前轮中不使用
//这样保证每轮只会松弛一次
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++){
int[]next=Arrays.copyOf(cur,n);
for(int[] edge:flights){
if(cur[edge[0]]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE){
//注意这里更新的数值用cur的,更新却放在next中
if(next[edge[1]]>cur[edge[0]]+edge[2]){
next[edge[1]]=cur[edge[0]]+edge[2];
}
}
}
cur=next;
}
return cur[dst]==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:cur[dst];
}
}
}4、负环
题目描述
给定一个 n 个点的有向图,请求出图中是否存在从顶点 1 出发能到达的负环。
负环的定义是:一条边权之和为负数的回路。 输入格式
本题单测试点有多组测试数据。
输入的第一行是一个整数 T,表示测试数据的组数。对于每组数据的格式如下:
第一行有两个整数,分别表示图的点数 n 和接下来给出边信息的条数 m。
接下来 m 行,每行三个整数 u, v, w。
若 w \geq 0,则表示存在一条从 u 至 v 边权为 w 的边,还存在一条从 v 至 u 边权为 w 的边。
若 w < 0,则只表示存在一条从 u 至 v 边权为 w 的边。
输出格式
对于每组数据,输出一行一个字符串,若所求负环存在,则输出 YES,否则输出 NO。
输入输出样例 #1
输入
2
3 4
1 2 2
1 3 4
2 3 1
3 1 -3
3 3
1 2 3
2 3 4
3 1 -8输出
NO
YES说明/提示
数据规模与约定
对于全部的测试点,保证:
1 \leq n \leq 2 \times 10^3
1 \leq m \leq 3 \times 10^3
1 \leq u, v \leq n
-10^4 \leq w \leq 10^4
1 \leq T \leq 10。
提示
请注意,m 不是图的边数。
这个题结合了 Bellman-Ford+SPFA 优化,同时求解的是一个负环问题,是一个很好的模版代码题 这份代码可用作 Bellman-Ford/Bellman-Ford+SPFA 的模版,也可以用做 Bellman-Ford+SPFA 求解负环的模版
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code04_SPFA
* @description: Bellman-Ford + SPFA优化模版(洛谷)
* // 给定n个点的有向图,请求出图中是否存在从顶点1出发能到达的负环
* // 负环的定义是:一条边权之和为负数的回路
* // 测试链接 : https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3385
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-27 13:21
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class065;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Code04_SPFA {
public static int MAXN = 2001;
public static int MAXM = 6001;
//链式前向星建图
public static int[] head = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] next = new int[MAXM];
public static int[] to = new int[MAXM];
public static int[] weight = new int[MAXM];
public static int cnt;
//接下来构造Bellman-Ford + SPFA需要的东西
public static int[] distance = new int[MAXN];
//SPFA需要从队列,用以后续每次更新只看上一轮有更新的点,不再看全部点
public static int MAXQ = 4000001;
public static int[] queue = new int[MAXQ];
public static boolean[] enter = new boolean[MAXN];
public static int l, r;
//为了判定是否出现负环
public static int[] updateCnt = new int[MAXN];
public static int n, m;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(bufferedReader);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
in.nextToken();
int t = (int) in.nval;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
in.nextToken();
n = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
m = (int) in.nval;
build();
for (int j = 0, u, v, w; j < m; j++) {
in.nextToken();
u = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
v = (int) in.nval;
in.nextToken();
w = (int) in.nval;
if (w >= 0) {
addEdge(u, v, w);
addEdge(v, u, w);
} else {
addEdge(u, v, w);
}
}
out.println(spfn() ? "YES" : "NO");
}
out.flush();
out.close();
bufferedReader.close();
}
public static void build() {
cnt = 1;
l = r = 0;
//数据给的都是从1开始计数
Arrays.fill(head, 1, n + 1, 0);
Arrays.fill(distance, 1, n + 1, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Arrays.fill(enter, 1, n + 1, false);
Arrays.fill(updateCnt, 1, n + 1, 0);
}
public static void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {
next[cnt] = head[u];
to[cnt] = v;
weight[cnt] = w;
head[u] = cnt++;
}
//重点Bellman-Ford + SPFA优化模版
public static boolean spfn() {
//题目问的是从1点出发是否能找到负环
//根据spfa的优化,每次Bellman-Ford只松弛有更新距离的点的边
//用一个队列存储上一轮更新过的点,enter判定那个点在这个队列中
distance[1] = 0;
queue[r++] = 1;
enter[1] = true;
//记录某个点被更新的次数
//在Bellman-Ford算法中我们写过,一个点到另外一个点的距离最多被松弛n-1次
//一旦超过这个次数,就说明出现负环,只有负环才能使得distance[P] + W < distance[S]一直成立,
//才能使得distance[P] + W不停的变小,不断的更新
updateCnt[1] += 1;
while (l < r) {
//弹出队列中的点
int cur = queue[l++];
//同时更新这个点从队列中弹出
enter[cur] = false;
//只更新队列中的点锁带来的边
for (int ei = head[cur], v, w; ei > 0; ei = next[ei]) {
v = to[ei];
w = weight[ei];
if (distance[cur] + w < distance[v]) {
distance[v] = distance[cur] + w;
//若这个点不在队列中
if (!enter[v]) {
updateCnt[v] += 1;
if (updateCnt[v] >= n) {
return true;
}
queue[r++] = v;
enter[v] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
}