核心思想
Dijkstra算法
Dijkstra 算法:给定一个源点,求解从源点到每个点的最短路径长度。单源最短路径算法。 适用范围:有向图、边的权值没有负数
彻底暴力的 Dijkstra 算法,不讲、时间复杂度太差、无意义
普通堆实现的 Dijkstra 算法,最普遍、最常用 算法核心过程: 节点弹出过就忽略 节点没弹出过,让其它没弹出节点距离变小的记录加入堆
反向索引堆实现的 Dijkstra 算法,最快速、最极致 核心在于掌握反向索引堆
对应本节题目 1、题目 2、题目 3
普通版
普通堆实现的 Dijkstra 算法,时间复杂度 O (m * log m),m 为边数
1、distance[i]表示从源点到 i 点的最短距离,visited[i]表示 i 节点是否从小根堆弹出过
2、准备好小根堆,小根堆存放记录:(x 点,源点到 x 的距离),小根堆根据距离组织
3、令 distance[源点]=0,(源点,0) 进入小根堆
4、从小根堆弹出 (u 点,源点到 u 的距离)
a. 如果 visited[u] == true,不做任何处理,重复步骤 4
b. 如果 visited[u] == false,令 visited[u] = true,u 就算弹出过了 然后考察 u 的每一条边,假设某边去往 v,边权为 w
1)如果 visited[v] == false 并且 distance[u] + w < distance[v]
令 distance[v] = distance[u] + w,把 (v, distance[u] + w) 加入小根堆
2)处理完 u 的每一条边之后,重复步骤 4
5、小根堆为空过程结束,distance 表记录了源点到每个节点的最短距离。
模版代码
class Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
//首先是建图
ArrayList<ArrayList<int[]>> graph=new ArrayList<>();
//初始化,注意测试用例给的数据都是从1开始的
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
//添加对应的边
for(int[] time:times){
graph.get(time[0]).add(new int[]{time[1],time[2]});
}
//构造距离数组,注意测试用例是从1开始计数,从1到N
int[]distance=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
distance[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
boolean[] visits=new boolean[n+1];
//准备普通的小根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->a[1]-b[1]);
//接下来开始Dijkstra算法
//初始化源点
distance[k]=0;
heap.add(new int[]{k,0});
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
int u=heap.poll()[0];
// 如果 visited[u] == true,不做任何处理,重复步骤 4
if(visits[u]){
continue;
}
//如果 visited[u] == false,令 visited[u] = true,u 就算弹出过了
visits[k]=true;
//考察u的每一条边
for(int[]edge:graph.get(u)){
//u->v
int v=edge[0];
//权重
int w=edge[1];
//如果 visited[v] == false 并且 distance[u] + w < distance[v]
//令 distance[v] = distance[u] + w,把 (v, distance[u] + w) 加入小根堆
if(distance[u]+w<distance[v]){
distance[v]=distance[u]+w;
heap.add(new int[]{v,distance[u]+w});
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans=Math.max(ans,distance[i]);
}
//若有无法到达的点则distance数组中必有一个代价为Integer.MAX_VALUE的点
return ans==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:ans;
}优化版
反向索引堆实现的 Dijkstra 算法,时间复杂度 O (m * log n),n 为节点数,m 为边数
1、准备好反向索引堆,根据源点到当前点的距离组织小根堆,可以做到如下操作
a. 新增记录 (x, 源点到 x 的距离)
b. 当源点到 x 的距离更新时,可以进行堆的调整
c. x 点一旦弹出,以后忽略 x
d. 弹出堆顶的记录 (u, 源点到 u 的距离)
2、把 (源点,0) 加入反向索引堆,过程开始
3、反向索引堆弹出 (u,源点到 u 的距离),考察 u 的每一条边,假设某边去往 v,边权为 w
1)如果 v 没有进入过反向索引堆里,新增记录 (v, 源点到 u 的距离 + w)
2)如果 v 曾经从反向索引堆弹出过,忽略
3)如果 v 在反向索引堆里,看看源点到 v 的距离能不能变得更小,如果能,调整堆;不能,忽略
4)处理完 u 的每一条边,重复步骤 3
4 、反向索引堆为空过程结束。反向索引堆里记录了源点到每个节点的最短距离。
模版代码
//Dijkstra算法优化版本:反向索引堆+链式前向星建图
class Solution2 {
public static int MAXN=101;
public static int MAXM=6001;
//链式前向星
public static int[]head=new int[MAXN];
public static int[]next=new int[MAXM];
public static int[]to=new int[MAXM];
public static int[]weight=new int[MAXM];
public static int cnt;
//反向索引堆
public static int[]heap=new int[MAXN];
// where[v] = -1,表示v这个节点,从来没有进入过堆
// where[v] = -2,表示v这个节点,已经弹出过了
// where[v] = i(>=0),表示v这个节点,在堆上的i位置
public static int[]where=new int[MAXN];
public static int heapSize;
public static int[]distance=new int[MAXN];
public static int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
build(n);
//链式前向星建图
for(int[]edge:times){
addEdge(edge[0],edge[1],edge[2]);
}
//开始 Dijkstra算法
//源点进入
addOrUpdateOrIgnore(k,0);
while(!isEmpty()){
int u=pop();
for(int ei=head[u];ei>0;ei=next[ei]){
addOrUpdateOrIgnore(to[ei],distance[u]+weight[ei]);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans=Math.max(ans,distance[i]);
}
return ans==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:ans;
}
public static void build(int n){
cnt=1;
heapSize=0;
Arrays.fill(head,0,n+1,0);
Arrays.fill(where,0,n+1,-1);
Arrays.fill(distance,0,n+1,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public static void addEdge(int u,int v,int w){
next[cnt]=head[u];
to[cnt]=v;
weight[cnt]=w;
head[u]=cnt++;
}
//反向堆索引优化
/**
3,反向索引堆弹出 (u,源点到 u 的距离),考察 u 的每一条边,假设某边去往 v,边权为 w
1)如果 v 没有进入过反向索引堆里,新增记录 (v, 源点到 u 的距离 + w)
2)如果 v 曾经从反向索引堆弹出过,忽略
3)如果 v 在反向索引堆里,看看源点到 v 的距离能不能变得更小,如果能,调整堆;不能,忽略
4)处理完 u 的每一条边,重复步骤 3
4 反向索引堆为空过程结束。反向索引堆里记录了源点到每个节点的最短距离。
*/
public static void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(int v,int c){
if(where[v]==-1){
//将点加入堆中
heap[heapSize]=v;
where[v]=heapSize++;
distance[v]=c;
//新加入的点要网上看,使堆为小根堆
heapInsert(where[v]);
}else if(where[v]>=0){
distance[v]=Math.min(distance[v],c);
heapInsert(where[v]);
}
}
public static void heapInsert(int i){
while(distance[heap[i]]<distance[heap[(i-1)/2]]){
swap(i,(i-1)/2);
i=(i-1)/2;
}
}
public static boolean isEmpty(){
return heapSize==0;
}
public static int pop(){
int ans=heap[0];
//要复原小根堆
swap(0,--heapSize);
heapify(0);
//弹出后的点标记,后续有关这个点的所有操作都不再处理
where[ans]=-2;
return ans;
}
public static void heapify(int i){
int l=i*2+1;
while(l<heapSize){
int best=l+1<heapSize && distance[heap[l+1]]<distance[heap[l]]?l+1:l;
best=distance[heap[best]]<distance[heap[i]]?best:i;
if(best==i){
break;
}
swap(i,best);
i=best;
l=2*i+1;
}
}
public static void swap(int i,int j){
//首先是堆中交换
int tmp=heap[i];
heap[i]=heap[j];
heap[j]=tmp;
//不要忘记索引数组的交换
where[heap[i]]=i;
where[heap[j]]=j;
}
}分层图最短路
分层图最短路,又叫扩点最短路
不把实际位置看做图上的点,而是把实际位置及其状态的组合看做是图上的点,然后搜索 Bfs 或者 Dijkstra 的过程不变,只是扩了点(分层)而已 原理简单,核心在于如何扩点、如何到达、如何算距离,每个题可能都不一样
对应本节题目 4、题目 5、题目 6
例题
1、网络延迟时间
题目描述: 有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中 ui 是源节点,vi 是目标节点, wi 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
示例 1:

输入:times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 输出:1
示例 3:
输入:times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 输出:-1
提示:
1 <= k <= n <= 1001 <= times.length <= 6000times[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi0 <= wi <= 100所有
(ui, vi)对都 互不相同(即,不含重复边)
Dijkstra 算法普通版:
class Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
//首先是建图
ArrayList<ArrayList<int[]>> graph=new ArrayList<>();
//初始化,注意测试用例给的数据都是从1开始的
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
//添加对应的边
for(int[] time:times){
graph.get(time[0]).add(new int[]{time[1],time[2]});
}
//构造距离数组,注意测试用例是从1开始计数,从1到N
int[]distance=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
distance[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
boolean[] visits=new boolean[n+1];
//准备普通的小根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->a[1]-b[1]);
//接下来开始Dijkstra算法
//初始化源点
distance[k]=0;
heap.add(new int[]{k,0});
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
int u=heap.poll()[0];
// 如果 visited[u] == true,不做任何处理,重复步骤 4 if(visits[u]){
continue;
}
//如果 visited[u] == false,令 visited[u] = true,u 就算弹出过了
visits[k]=true;
//考察u的每一条边
for(int[]edge:graph.get(u)){
//u->v
int v=edge[0];
//权重
int w=edge[1];
//如果 visited[v] == false 并且 distance[u] + w < distance[v] //令 distance[v] = distance[u] + w,把 (v, distance[u] + w) 加入小根堆
if(distance[u]+w<distance[v]){
distance[v]=distance[u]+w;
heap.add(new int[]{v,distance[u]+w});
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans=Math.max(ans,distance[i]);
}
//若有无法到达的点则distance数组中必有一个代价为Integer.MAX_VALUE的点
return ans==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:ans;
}Dijkstra 算法优化版
//Dijkstra算法优化版本:反向索引堆+链式前向星建图
class Solution2 {
public static int MAXN=101;
public static int MAXM=6001;
//链式前向星
public static int[]head=new int[MAXN];
public static int[]next=new int[MAXM];
public static int[]to=new int[MAXM];
public static int[]weight=new int[MAXM];
public static int cnt;
//反向索引堆
public static int[]heap=new int[MAXN];
// where[v] = -1,表示v这个节点,从来没有进入过堆
// where[v] = -2,表示v这个节点,已经弹出过了
// where[v] = i(>=0),表示v这个节点,在堆上的i位置
public static int[]where=new int[MAXN];
public static int heapSize;
public static int[]distance=new int[MAXN];
public static int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
build(n);
//链式前向星建图
for(int[]edge:times){
addEdge(edge[0],edge[1],edge[2]);
}
//开始 Dijkstra算法
//源点进入
addOrUpdateOrIgnore(k,0);
while(!isEmpty()){
int u=pop();
for(int ei=head[u];ei>0;ei=next[ei]){
addOrUpdateOrIgnore(to[ei],distance[u]+weight[ei]);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans=Math.max(ans,distance[i]);
}
return ans==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:ans;
}
public static void build(int n){
cnt=1;
heapSize=0;
Arrays.fill(head,0,n+1,0);
Arrays.fill(where,0,n+1,-1);
Arrays.fill(distance,0,n+1,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public static void addEdge(int u,int v,int w){
next[cnt]=head[u];
to[cnt]=v;
weight[cnt]=w;
head[u]=cnt++;
}
//反向堆索引优化
/**
3,反向索引堆弹出 (u,源点到 u 的距离),考察 u 的每一条边,假设某边去往 v,边权为 w
1)如果 v 没有进入过反向索引堆里,新增记录 (v, 源点到 u 的距离 + w)
2)如果 v 曾经从反向索引堆弹出过,忽略
3)如果 v 在反向索引堆里,看看源点到 v 的距离能不能变得更小,如果能,调整堆;不能,忽略
4)处理完 u 的每一条边,重复步骤 3
4 反向索引堆为空过程结束。反向索引堆里记录了源点到每个节点的最短距离。
*/
public static void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(int v,int c){
if(where[v]==-1){
//将点加入堆中
heap[heapSize]=v;
where[v]=heapSize++;
distance[v]=c;
//新加入的点要网上看,使堆为小根堆
heapInsert(where[v]);
}else if(where[v]>=0){
distance[v]=Math.min(distance[v],c);
heapInsert(where[v]);
}
}
public static void heapInsert(int i){
while(distance[heap[i]]<distance[heap[(i-1)/2]]){
swap(i,(i-1)/2);
i=(i-1)/2;
}
}
public static boolean isEmpty(){
return heapSize==0;
}
public static int pop(){
int ans=heap[0];
//要复原小根堆
swap(0,--heapSize);
heapify(0);
//弹出后的点标记,后续有关这个点的所有操作都不再处理
where[ans]=-2;
return ans;
}
public static void heapify(int i){
int l=i*2+1;
while(l<heapSize){
int best=l+1<heapSize && distance[heap[l+1]]<distance[heap[l]]?l+1:l;
best=distance[heap[best]]<distance[heap[i]]?best:i;
if(best==i){
break;
}
swap(i,best);
i=best;
l=2*i+1;
}
}
public static void swap(int i,int j){
//首先是堆中交换
int tmp=heap[i];
heap[i]=heap[j];
heap[j]=tmp;
//不要忘记索引数组的交换
where[heap[i]]=i;
where[heap[j]]=j;
}
}2、最小体力消耗路径
题目描述: 你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights ,其中 heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1) (注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径。
一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值 。
示例 1:
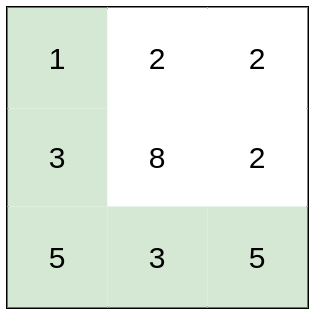
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] 输出:2 解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。 这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3 。
示例 2:
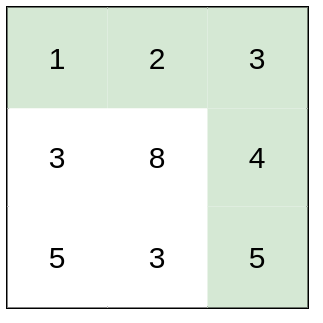
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] 输出:1 解释:路径 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相邻格子差值绝对值最大为 1 ,比路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 更优。
示例 3:
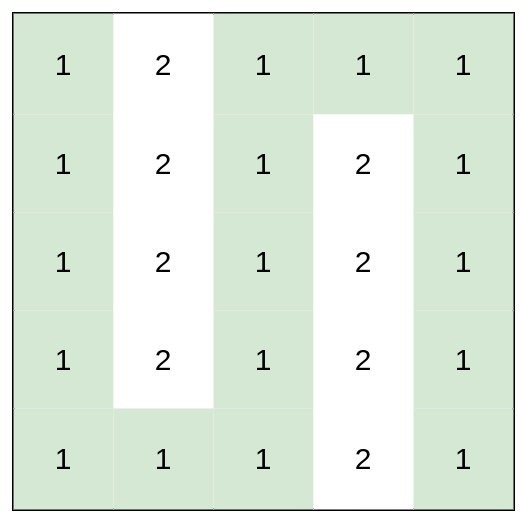
输入:heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] 输出:0 解释:上图所示路径不需要消耗任何体力。
提示:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code02_PathWithMinimumEffort
* @description: 最小体力消耗路径
* // 你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights
* // 其中 heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度
* // 一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1)
* // (注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右 四个方向之一移动
* // 你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径
* // 一条路径耗费的体力值是路径上,相邻格子之间高度差绝对值的最大值
* // 请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值
* // 测试链接 :https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-minimum-effort/
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-23 11:03
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class064;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Code02_PathWithMinimumEffort {
class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int[]move=new int[]{-1,0,1,0,-1};
int n=heights.length;
int m=heights[0].length;
boolean[][]visited=new boolean[n][m];
int[][]distance=new int[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
distance[0][0]=0;
//0:x
//1:y
//2: distance
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->a[2]-b[2]);
heap.add(new int[]{0,0,distance[0][0]});
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
int[]record=heap.poll();
int x=record[0];
int y=record[1];
int w=record[2];
if(visited[x][y]){
continue;
}
if(x==n-1 && y==m-1){
return w;
}
visited[x][y]=true;
//开始向四周扩散
for(int i=0,nx,ny,nw;i<4;i++){
nx=x+move[i];
ny=y+move[i+1];
if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m && !visited[nx][ny]){
nw=Math.max(w,Math.abs(heights[x][y]-heights[nx][ny]));
if(nw<distance[nx][ny]){
distance[nx][ny]=nw;
heap.add(new int[]{nx,ny,nw});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
}3、水位上升的泳池中游泳
题目描述: 在一个 n x n 的整数矩阵 grid 中,每一个方格的值 grid[i][j] 表示位置 (i, j) 的平台高度。
当开始下雨时,在时间为 t 时,水池中的水位为 t 。你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台。假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的。当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。
你从坐标方格的左上平台 (0,0) 出发。返回 你到达坐标方格的右下平台 (n-1, n-1) 所需的最少时间 。
示例 1:
输入: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]] 输出: 3 解释: 时间为0时,你位于坐标方格的位置为 (0, 0)。 此时你不能游向任意方向,因为四个相邻方向平台的高度都大于当前时间为 0 时的水位。 等时间到达 3 时,你才可以游向平台 (1, 1). 因为此时的水位是 3,坐标方格中的平台没有比水位 3 更高的,所以你可以游向坐标方格中的任意位置
示例 2:
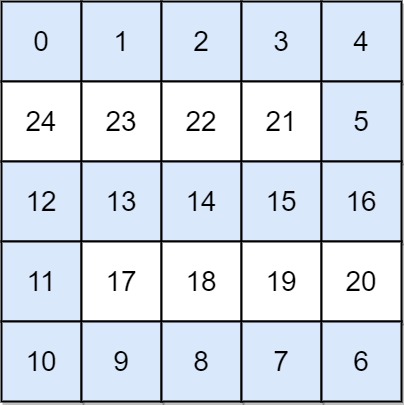
输入: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]] 输出: 16 解释: 最终的路线用加粗进行了标记。 我们必须等到时间为 16,此时才能保证平台 (0, 0) 和 (4, 4) 是连通的
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2grid[i][j]中每个值 均无重复
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code03_SwimInRisingWater
* @description: 水位上升的泳池中游泳
* // 在一个 n x n 的整数矩阵 grid 中
* // 每一个方格的值 grid[i][j] 表示位置 (i, j) 的平台高度
* // 当开始下雨时,在时间为 t 时,水池中的水位为 t
* // 你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台
* // 假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的
* // 当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。
* // 你从坐标方格的左上平台 (0,0) 出发
* // 返回 你到达坐标方格的右下平台 (n-1, n-1) 所需的最少时间
* // 测试链接 : https://leetcode.cn/problems/swim-in-rising-water/
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-24 09:29
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class064;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Code03_SwimInRisingWater {
class Solution {
public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) {
int[]move=new int[]{-1,0,1,0,-1};
int n=grid.length;
int[][]distance=new int[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
boolean[][]visited=new boolean[n][n];
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->a[2]-b[2]);
//开始Dijkstra算法
distance[0][0]=grid[0][0];
heap.add(new int[]{0,0,distance[0][0]});
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
int[]record=heap.poll();
int x=record[0];
int y=record[1];
int w=record[2];
if(visited[x][y]){
continue;
}
if(x==n-1 && y==n-1){
return w;
}
visited[x][y]=true;
for(int i=0,nx,ny,nw;i<4;i++){
nx=x+move[i];
ny=y+move[i+1];
if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<n && !visited[nx][ny]){
nw=Math.max(w,grid[nx][ny]);
if(nw<distance[nx][ny]){
distance[nx][ny]=nw;
heap.add(new int[]{nx,ny,distance[nx][ny]});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
}4、获取所有钥匙的最短路径
题目描述: 给定一个二维网格 grid ,其中:
'.' 代表一个空房间
'#' 代表一堵墙
'@' 是起点
小写字母代表钥匙
大写字母代表锁
我们从起点开始出发,一次移动是指向四个基本方向之一行走一个单位空间。我们不能在网格外面行走,也无法穿过一堵墙。如果途经一个钥匙,我们就把它捡起来。除非我们手里有对应的钥匙,否则无法通过锁。
假设 k 为 钥匙/锁 的个数,且满足 1 <= k <= 6,字母表中的前 k 个字母在网格中都有自己对应的一个小写和一个大写字母。换言之,每个锁有唯一对应的钥匙,每个钥匙也有唯一对应的锁。另外,代表钥匙和锁的字母互为大小写并按字母顺序排列。
返回获取所有钥匙所需要的移动的最少次数。如果无法获取所有钥匙,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
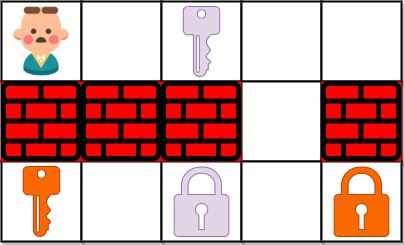
输入:grid = ["@.a..","###.#","b.A.B"] 输出:8 解释:目标是获得所有钥匙,而不是打开所有锁。
示例 2:
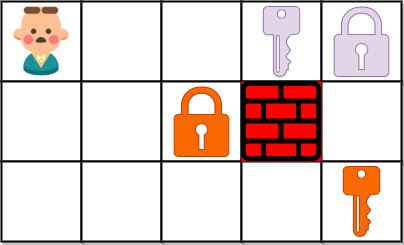
输入:grid = ["@..aA","..B#.","....b"] 输出:6
示例 3:

输入: grid = ["@Aa"] 输出: -1
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 30grid[i][j]只含有'.','#','@','a'-``'f``'以及'A'-'F'钥匙的数目范围是
[1, 6]每个钥匙都对应一个 不同 的字母
每个钥匙正好打开一个对应的锁
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code04_ShortestPathToGetAllKeys
* @description:获取所有钥匙的最短路径
* // 给定一个二维网格grid,其中:
* // '.' 代表一个空房间、'#' 代表一堵、'@'是起点
* // 小写字母代表钥匙、大写字母代表锁
* // 从起点开始出发,一次移动是指向四个基本方向之一行走一个单位空间
* // 不能在网格外面行走,也无法穿过一堵墙
* // 如果途经一个钥匙,我们就把它捡起来。除非我们手里有对应的钥匙,否则无法通过锁。
* // 假设 k为 钥匙/锁 的个数,且满足1 <= k<= 6,
* // 字母表中的前 k个字母在网格中都有自己对应的一个小写和一个大写字母
* // 换言之,每个锁有唯一对应的钥匙,每个钥匙也有唯一对应的锁
* // 另外,代表钥匙和锁的字母互为大小写并按字母顺序排列
* // 返回获取所有钥匙所需要的移动的最少次数。如果无法获取所有钥匙,返回-1。
* // 测试链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-path-to-get-all-keys
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-24 10:02
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class064;
public class Code04_ShortestPathToGetAllKeys {
class Solution {
public static int MAXM=31;
public static int MAXN=31;
public static int MAXK=6;
//图的网格
public static char[][] grid=new char[MAXM][];
//是否经过某个点的某个状态
public static boolean[][][]visited=new boolean[MAXM][MAXN][1<<MAXK];
//队列
//0:x
//1: y //2: 当前的状态(身上的有哪些钥匙)
public static int[][]queue=new int[MAXM*MAXN*(1<<MAXK)][3];
public static int l,r,n,m,key;
public static int[]move=new int[]{-1,0,1,0,-1};
public int shortestPathAllKeys(String[] g) {
build(g);
int level=1;
//bfs
while(l<r){
int size=r-l;
for(int k=0,x,y,s;k<size;k++){
//当前状态
x=queue[l][0];
y=queue[l][1];
s=queue[l++][2];
//向四周寻找
for(int i=0,nx,ny,ns;i<4;i++){
nx=x+move[i];
ny=y+move[i+1];
ns=s;
//如果越界或者撞到了墙上,则此路不通
if(nx<0 || nx>=m || ny<0 || ny>=n || grid[nx][ny]=='#'){
continue;
}
//如果遇到了锁,但是身上并没有其钥匙,那么此路不通
if(grid[nx][ny]>='A' && grid[nx][ny]<='F' && (ns&(1<<(grid[nx][ny]-'A')))==0){
continue;
}
//如果遇到一把钥匙,则收集
if(grid[nx][ny]>='a' && grid[nx][ny]<='f'){
ns|=(1<<(grid[nx][ny]-'a'));
}
//如果钥匙收集全了,则直接返回结果,一个剪枝步骤
if(ns==key){
return level;
}
//如果当前点状态未被参观,则加入参观,同时将其近期如队列
if(!visited[nx][ny][ns]){
visited[nx][ny][ns]=true;
queue[r][0]=nx;
queue[r][1]=ny;
queue[r++][2]=ns;
}
}
}
level++;
}
return -1;
}
public static void build(String[]g){
//首先将字符数组转换为char的网格二维数组
m=g.length;
n=g[0].length();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
grid[i]=g[i].toCharArray();
}
l=r=key=0;
//找到初始位置出发点、钥匙收集全的状态
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
//找到初始位置
if(grid[i][j]=='@'){
queue[r][0]=i;
queue[r][1]=j;
queue[r++][2]=0;
}
//收集钥匙的状态
if(grid[i][j]>='a' && grid[i][j]<='f'){
key|=1<<(grid[i][j]-'a');
}
}
}
//visited数组的遍历状态
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
for(int s=0;s<=key;s++){
visited[i][j][s]=false;
}
}
}
}
}
}5、电动车游城市
题目描述: 小明的电动车电量充满时可行驶距离为 cnt,每行驶 1 单位距离消耗 1 单位电量,且花费 1 单位时间。小明想选择电动车作为代步工具。地图上共有 N 个景点,景点编号为 0 ~ N-1。他将地图信息以 [城市 A 编号,城市 B 编号,两城市间距离] 格式整理在在二维数组 paths,表示城市 A、B 间存在双向通路。初始状态,电动车电量为 0。每个城市都设有充电桩,charge[i] 表示第 i 个城市每充 1 单位电量需要花费的单位时间。请返回小明最少需要花费多少单位时间从起点城市 start 抵达终点城市 end。
示例 1:
输入:paths = [[1,3,3],[3,2,1],[2,1,3],[0,1,4],[3,0,5]], cnt = 6, start = 1, end = 0, charge = [2,10,4,1] 输出:43 解释:最佳路线为:1->3->0。 在城市 1 仅充 3 单位电至城市 3,然后在城市 3 充 5 单位电,行驶至城市 0。 充电用时共 310 + 51= 35 行驶用时 3 + 5 = 8,此时总用时最短 43。
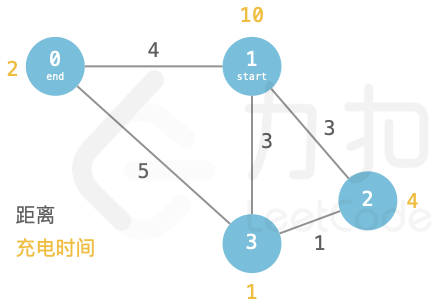
示例 2:
输入:paths = [[0,4,2],[4,3,5],[3,0,5],[0,1,5],[3,2,4],[1,2,8]], cnt = 8, start = 0, end = 2, charge = [4,1,1,3,2] 输出:38 解释:最佳路线为:0->4->3->2。 城市 0 充电 2 单位,行驶至城市 4 充电 8 单位,行驶至城市 3 充电 1 单位,最终行驶至城市 2。 充电用时 42+28+3*1 = 27 行驶用时 2+5+4 = 11,总用时最短 38。
提示:
1 <= paths.length <= 200paths[i].length == 32 <= charge.length == n <= 1000 <= path[i][0],path[i][1],start,end < n1 <= cnt <= 1001 <= path[i][2] <= cnt1 <= charge[i] <= 100题目保证所有城市相互可以到达
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code05_VisitCityMinCost
* @description: 电动车游城市
* // 小明的电动车电量充满时可行驶距离为 cnt,每行驶 1 单位距离消耗 1 单位电量,且花费 1 单位时间
* // 小明想选择电动车作为代步工具。地图上共有 N 个景点,景点编号为 0 ~ N-1
* // 他将地图信息以 [城市 A 编号,城市 B 编号,两城市间距离] 格式整理在在二维数组 paths,
* // 表示城市 A、B 间存在双向通路。
* // 初始状态,电动车电量为 0。每个城市都设有充电桩,
* // charge[i] 表示第 i 个城市每充 1 单位电量需要花费的单位时间。
* // 请返回小明最少需要花费多少单位时间从起点城市 start 抵达终点城市 end
* // 测试链接 : https://leetcode.cn/problems/DFPeFJ/
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-24 11:24
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class064;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Code05_VisitCityMinCost {
class Solution {
public int electricCarPlan(int[][] paths, int cnt, int start, int end, int[] charge) {
int n=charge.length;
//建图
ArrayList<ArrayList<int[]>>graph=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int[] path:paths){
//注意是无向图
graph.get(path[0]).add(new int[]{path[1],path[2]});
graph.get(path[1]).add(new int[]{path[0],path[2]});
}
//距离数组
//这里的距离是代价,由于每个城市对应的电动车的电量可以有cnt种
//因此这里每个点指的不再是城市或者道路节点,而是到达某个城市时自身拥有的一个状态为一个点(电动车电量)
//由于电量是1-cnt因此数组要有cnt+1个才能对应装
int[][]distance=new int[n][cnt+1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=cnt;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
//构建参观数组
boolean [][]visited=new boolean[n][cnt+1];
//由于题目本质还是找花费最小代价的最短路径问题,且题目边的权重不同,因此用Dijkstra算法
//0:城市点;1:电量;2:代价
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->a[2]-b[2]);
//由于初始状态电动车无电
distance[start][0]=0;
heap.add(new int[]{start,0,distance[start][0]});
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
int[]record=heap.poll();
//当前城市
int cur=record[0];
//当前电量
int power=record[1];
//代价
int cost=record[2];
if(visited[cur][power]){
continue;
}
if(cur==end){
return cost;
}
visited[cur][power]=true;
//接下来就是这个题目的关键,这也是分层最短路径与普通的寻找最短路径最大的区别,本身带有太多状态的考量
//当前点充电否,是不充电直接开往下一个城市,还是充电开往下一个城市,充电充多少
//如果充电,我们每次充一格点加入heap小根堆,后续每次弹出都会再充一格点直到状态遍历完
if(power+1<=cnt && !visited[cur][power+1]){
if(cost+charge[cur]<distance[cur][power+1]){
distance[cur][power+1]=cost+charge[cur];
heap.add(new int[]{cur,power+1,distance[cur][power+1]});
}
}
//不充电直接开往下一个城市
for(int[]path:graph.get(cur)){
int nextCity=path[0];
int nextPower=power-path[1];
int nextCost=cost+path[1];
if(nextPower>=0 && !visited[nextCity][nextPower]&& nextCost < distance[nextCity][nextPower]){
heap.add(new int[]{nextCity,nextPower,nextCost});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
}6、飞行路线
题目描述
Alice 和 Bob 现在要乘飞机旅行,他们选择了一家相对便宜的航空公司。该航空公司一共在 n 个城市设有业务,设这些城市分别标记为 0 到 n-1,一共有 m 种航线,每种航线连接两个城市,并且航线有一定的价格。
Alice 和 Bob 现在要从一个城市沿着航线到达另一个城市,途中可以进行转机。航空公司对他们这次旅行也推出优惠,他们可以免费在最多 k 种航线上搭乘飞机。那么 Alice 和 Bob 这次出行最少花费多少? 输入格式
第一行三个整数 n,m,k,分别表示城市数,航线数和免费乘坐次数。
接下来一行两个整数 s,t,分别表示他们出行的起点城市编号和终点城市编号。
接下来 m 行,每行三个整数 a,b,c,表示存在一种航线,能从城市 a 到达城市 b,或从城市 b 到达城市 a,价格为 c。
输出格式
输出一行一个整数,为最少花费。
输入输出样例
输入
5 6 1
0 4
0 1 5
1 2 5
2 3 5
3 4 5
2 3 3
0 2 100输出
8说明/提示
数据规模与约定
对于 30\% 的数据,2 \le n \le 50,1 \le m \le 300,k=0。
对于 50\% 的数据,2 \le n \le 600,1 \le m \le 6\times10^3,0 \le k \le 1。
对于 100\% 的数据,2 \le n \le 10^4,1 \le m \le 5\times 10^4,0 \le k \le 10,0\le s,t,a,b < n,a\ne b,0\le c\le 10^3。
另外存在一组 hack 数据。
/**
* @program: ZuoChengxunAlgorithmClass
* @ClassName Code06_FlightPath1
* @description:飞行路线(语言提供的堆)
* // Alice和Bob现在要乘飞机旅行,他们选择了一家相对便宜的航空公司
* // 该航空公司一共在n个城市设有业务,设这些城市分别标记为0 ~ n−1
* // 一共有m种航线,每种航线连接两个城市,并且航线有一定的价格
* // Alice 和 Bob 现在要从一个城市沿着航线到达另一个城市,途中可以进行转机
* // 航空公司对他们这次旅行也推出优惠,他们可以免费在最多k种航线上搭乘飞机
* // 那么 Alice 和 Bob 这次出行最少花费多少
* // 测试链接 : https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4568
* @author: zs宝
* @create: 2025-07-25 10:45
* @Version 1.0
**/
package main.java.class064;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Code06_FlightPath {
public static int MAXN=10001;
//注意无向图,最大的边数*2
public static int MAXM=100001;
public static int MAXK=11;
public static int n,m,k,start,end;
//建图的链式前向星
public static int[]head=new int[MAXN];
public static int[]next=new int[MAXM];
public static int[]to=new int[MAXM];
public static int[]weight=new int[MAXM];
public static int cnt;
//代价数组
//在某个城市乘坐了第几次免费航线,当前的代价是多少
//这里的点是城市+乘坐免费航线次数的组合
public static int[][]distance=new int[MAXN][MAXK];
public static boolean[][] visited = new boolean[MAXN][MAXK];
//Dijkstra算法的小根堆
//自己写的堆优化
public static int[][]heap=new int[MAXN*MAXK][3];
public static int heapSize;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StreamTokenizer in=new StreamTokenizer(bufferedReader);
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while (in.nextToken()!=StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF){
n=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
m=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
k=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
start=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
end=(int)in.nval;
build();
for(int i=0,a,b,c;i<m;i++){
in.nextToken();
a=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
b=(int)in.nval;
in.nextToken();
c=(int)in.nval;
addEdge(a,b,c);
addEdge(b,a,c);
}
out.println(dijkstra());
}
out.flush();
out.close();
bufferedReader.close();
}
public static void build(){
//链式前向星初始化
cnt=1;
Arrays.fill(head,0,n+1,0);
//距离数组初始化
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=k;j++){
distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
visited[i][j]=false;
}
}
//堆初始化
heapSize=0;
}
//链式前向星加边
public static void addEdge(int u,int v,int w){
next[cnt]=head[u];
to[cnt]=v;
weight[cnt]=w;
head[u]=cnt++;
}
//用来代表小根堆每次弹出的节点中的数据
public static int cur,use,cost;
public static int dijkstra(){
distance[start][0]=0;
//小根堆加入
push(start,0,0);
while(!isEmpty()){
//弹出小根堆根节点
pop();
if(visited[cur][use]){
continue;
}
if(cur==end){
return cost;
}
visited[cur][use]=true;
//对于下一段航线,分别尝试使用免费和不适用免费
for(int ei=head[cur];ei>0;ei=next[ei]){
int next = to[ei];
int w=weight[ei];
//使用免费
if(use<k && !visited[next][use+1] && distance[cur][use]<distance[next][use+1]){
distance[next][use+1]=distance[cur][use];
push(next,use+1,distance[next][use+1]);
}
//不使用免费
if(!visited[next][use] && distance[cur][use]+w<distance[next][use]){
distance[next][use]=distance[cur][use]+w;
push(next,use,distance[next][use]);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void push(int u,int t,int c){
heap[heapSize][0]=u;
heap[heapSize][1]=t;
heap[heapSize][2]=c;
heapInsert(heapSize++);
}
public static void heapInsert(int i){
while (i>0 && heap[i][2]<heap[(i-1)/2][2]){
swap(i,(i-1)/2);
i=(i-1)/2;
}
}
public static void swap(int i,int j){
int[]temp=heap[i];
heap[i]=heap[j];
heap[j]=temp;
}
public static void pop(){
cur=heap[0][0];
use=heap[0][1];
cost=heap[0][2];
swap(0,--heapSize);
heapfy(0);
}
public static void heapfy(int i){
int l=2*i+1;
while (l<heapSize){
int best=(l+1)<heapSize && heap[l+1][2]<heap[l][2]?l+1:l;
best=heap[best][2]<heap[i][2]?best:i;
if(best==i){
break;
}
swap(best,i);
i=best;
l=2*i+1;
}
}
public static boolean isEmpty(){
return heapSize==0;
}
}